In the rapidly evolving landscape of Industry 4.0, digital transformation has become a cornerstone for enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality. At the forefront of this revolution is the concept of the digital twin. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object, system, or process that uses real-time data to mirror its counterpart’s behaviour and performance. This technology has been gaining traction across various sectors, including manufacturing, energy, logistics, and healthcare. By simulating real-world processes, digital twins provide insights that facilitate better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and enhanced collaboration. This article explores how digital twins are transforming industrial processes, their applications, benefits, and the challenges associated with their implementation.
Understanding Digital Twins

What is a Digital Twin?
A digital twin encompasses the physical object’s characteristics, behaviours, and states. It leverages Internet of Things (IoT) technology, data analytics, and machine learning to create a dynamic model that evolves alongside its physical counterpart. By integrating sensors and data collection devices, digital twins provide a continuous flow of information that can be analyzed to gain insights into performance metrics, identify potential issues, and optimize processes.
The Components of a Digital Twin
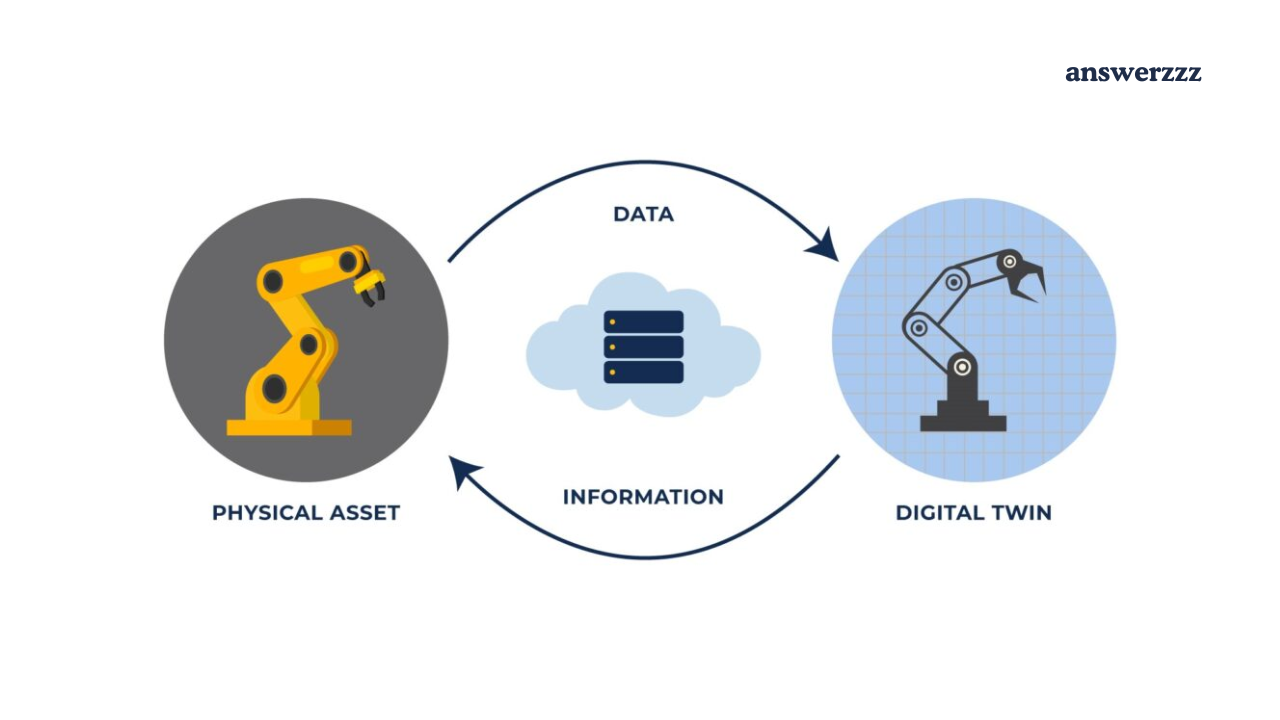
- Physical Asset: The actual machine or system being monitored, such as a turbine, manufacturing line, or vehicle.
- Digital Representation: A virtual model that mirrors the physical asset, incorporating data on design, behaviour, and operational performance.
- Data Connection: A network that facilitates the flow of real-time data from the physical asset to the digital twin.
- Analytics and Simulation Tools: Software applications that process data, enabling analysis and predictive modelling.
Applications of Digital Twins in Industrial Processes
1. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is one of the most significant applications of digital twins. By analyzing real-time data from sensors embedded in machinery, organizations can anticipate when equipment is likely to fail. This proactive approach allows companies to schedule maintenance activities before failures occur, thereby minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
For example, in manufacturing plants, digital twins can predict equipment failures by monitoring vibration, temperature, and other performance metrics. This capability helps operators take timely actions, such as replacing parts or adjusting settings, to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
2. Process Optimization
Digital twins enable continuous optimization of industrial processes. By simulating different scenarios and analyzing the outcomes, organizations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. This iterative approach allows for the fine-tuning of operations, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity.
For instance, in the automotive industry, digital twins are used to simulate production lines, testing various configurations and workflows. This allows manufacturers to determine the most efficient layout, leading to faster production times and reduced waste.
3. Product Development and Design
Digital twins play a crucial role in product development, allowing engineers and designers to test and iterate on designs in a virtual environment before physical prototypes are created. This not only speeds up the development cycle but also reduces costs associated with material waste and production.
In industries such as aerospace, where design complexity and safety are paramount, digital twins allow for extensive testing and validation of components under various conditions, ensuring they meet regulatory standards and performance expectations.
4. Supply Chain Management
Digital twins are increasingly being utilized in supply chain management to improve visibility and responsiveness. By creating a digital twin of the entire supply chain, organizations can monitor inventory levels, transportation logistics, and supplier performance in real time. This holistic view enables companies to make informed decisions about inventory management, demand forecasting, and supply chain optimization.
For example, companies like Amazon employ digital twin technology to enhance their fulfilment centres’ efficiency. By simulating order processing and warehouse operations, they can identify ways to streamline workflows, reduce delivery times, and improve customer satisfaction.
5. Workforce Training and Safety
Digital twins can also be leveraged for training purposes, providing employees with immersive, hands-on experiences in a safe virtual environment. This application is particularly valuable in industries where operating heavy machinery or working in hazardous conditions is common.
By simulating real-world scenarios, workers can practice their skills and learn to handle emergencies without risking their safety. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, workers can train on digital twins of drilling rigs, preparing them for various situations they may encounter in the field.
Benefits of Digital Twins in Industrial Processes

1. Enhanced Decision-Making
With access to real-time data and predictive analytics, decision-makers can make informed choices that drive efficiency and performance. Digital twins enable organizations to visualize complex processes, making it easier to identify trends and insights that inform strategic planning.
2. Cost Reduction
By implementing predictive maintenance and process optimization strategies, organizations can significantly reduce operational costs. Fewer unplanned downtimes, lower maintenance expenses, and optimized resource allocation contribute to overall cost savings.
3. Improved Product Quality
Digital twins facilitate thorough testing and simulation, enabling companies to identify design flaws and potential issues before production. This proactive approach results in higher-quality products that meet customer expectations and regulatory standards.
4. Increased Agility
In today’s fast-paced business environment, agility is essential for staying competitive. Digital twins allow organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, customer demands, and operational challenges. By continuously monitoring and optimizing processes, companies can adapt their strategies in real-time.
5. Better Collaboration
Digital twins promote collaboration across different departments and teams by providing a shared understanding of processes and systems. By centralizing data and insights, stakeholders can work together more effectively, breaking down silos and fostering innovation.
Challenges of Implementing Digital Twins
Despite their numerous benefits, the implementation of digital twins in industrial processes is not without challenges. Organizations must navigate several hurdles to successfully adopt this technology.
1. Data Integration
One of the primary challenges is integrating data from various sources, including legacy systems, IoT devices, and enterprise software. Organizations must develop a robust data infrastructure that enables seamless data flow and real-time updates.
2. Complexity of Models
Creating accurate and comprehensive digital twins requires sophisticated modelling techniques and tools. Organizations may struggle with the complexity involved in developing digital twins that accurately represent their physical counterparts.
3. Skill Gaps
The successful implementation of digital twins demands a workforce skilled in data analytics, machine learning, and software development. Organizations may face challenges in recruiting and retaining talent with the necessary expertise.
4. Security Concerns
With increased connectivity and data sharing, organizations must also address security concerns related to data privacy and cyber threats. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity.
5. Initial Investment
The initial investment in technology, infrastructure, and training can be significant. Organizations must weigh the upfront costs against the long-term benefits of adopting digital twin technology.
Future Trends in Digital Twins

As technology continues to evolve, the applications and capabilities of digital twins will expand. Several trends are shaping the future of this technology in industrial processes.
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with digital twins will enhance their predictive capabilities and decision-making processes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, enabling more accurate predictions and recommendations.
2. Greater Interoperability
As industries adopt digital twin technology, the demand for interoperability among different systems and platforms will grow. Future digital twins will need to communicate seamlessly with other digital twins and IoT devices, enabling a more cohesive ecosystem.
3. Advanced Simulation Techniques
Advancements in simulation techniques will allow for more realistic modelling of complex systems. This will enhance the accuracy of digital twins and improve their effectiveness in optimizing industrial processes.
4. Widespread Adoption Across Industries
While digital twins have made significant inroads in manufacturing and aerospace, other industries, such as healthcare, agriculture, and construction, are beginning to recognize their potential. As awareness grows, the adoption of digital twins is expected to increase across various sectors.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
As industries become more focused on sustainability, digital twins will play a critical role in optimizing resource usage and minimizing waste. By simulating environmental impacts and assessing sustainability metrics, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their environmental goals.
Digital twins are revolutionizing industrial processes by providing organizations with valuable insights, enabling predictive maintenance, optimizing operations, and improving product quality. Despite the challenges associated with their implementation, the benefits of digital twins far outweigh the drawbacks. As technology continues to advance, the applications and capabilities of digital twins will expand, paving the way for a more efficient and agile industrial landscape. By embracing this transformative technology, organizations can position themselves for success in the competitive world of Industry 4.0, driving innovation and achieving sustainable growth.