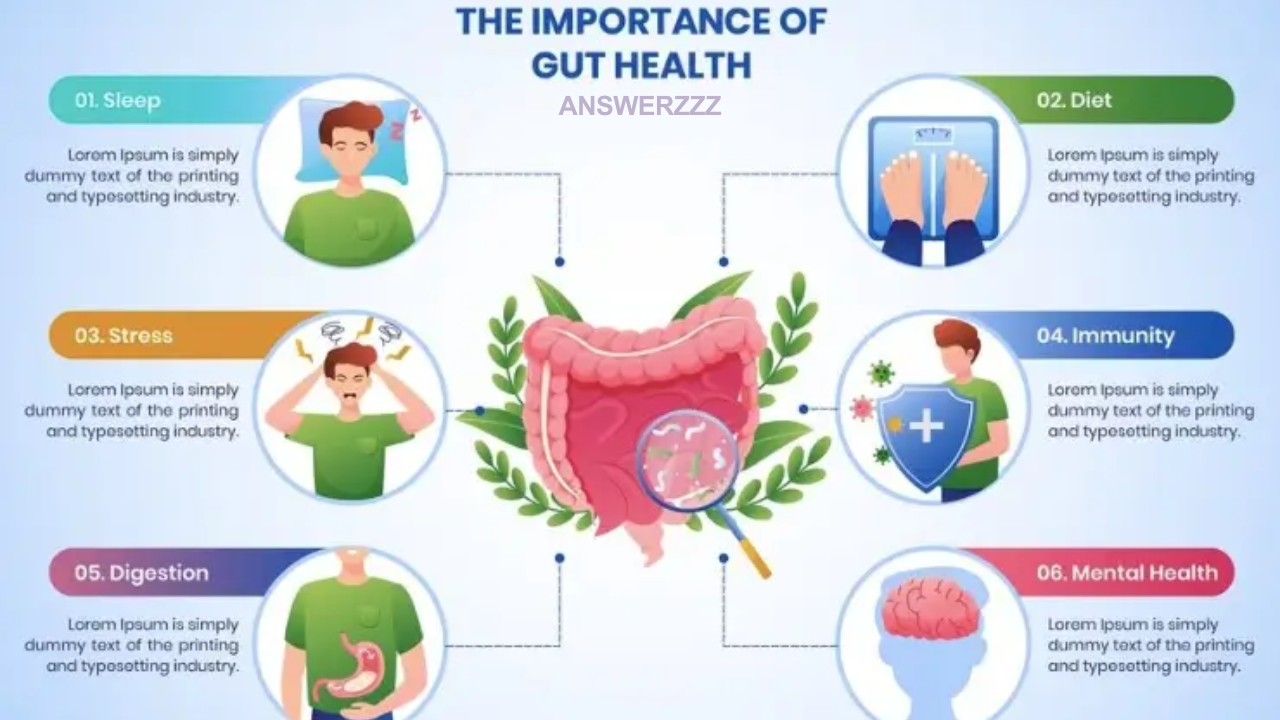
The term “gut health” has become a buzzword in recent years, capturing the attention of health enthusiasts, scientists, and everyday people alike. It’s no wonder, as research continues to unveil the pivotal role the gut plays in maintaining overall health and well-being. Far from being just a digestive organ, the gut is a central hub that influences immunity, mental health, metabolism, and even skin health.
In this comprehensive blog, we’ll explore what gut health means, why it’s crucial, how it impacts your body, and practical steps to improve and maintain a healthy gut.
What Is Gut Health?
At its core, gut health refers to the balance and optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This includes everything from the stomach to the intestines, where food is digested, nutrients are absorbed, and waste is expelled. However, gut health is about much more than digestion—it’s deeply connected to a community of trillions of microorganisms known as the gut microbiome.

The Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome consists of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes that live in your digestive system. While some of these microorganisms are harmful, the majority are beneficial and play critical roles in:
- Digesting food: Breaking down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Producing vitamins: Generating essential nutrients like Vitamin B12, K2, and short-chain fatty acids.
- Regulating the immune system: Training your immune system to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances.
- Protecting against pathogens: Competing with harmful microbes to prevent infections.
- Supporting mental health: Influencing the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin.
A healthy gut is characterized by a diverse microbiome, with a balance between beneficial and potentially harmful microorganisms.
The Importance of Gut Health
Your gut is often referred to as your “second brain” due to its extensive impact on various bodily functions. Here’s why maintaining gut health is essential:
1. Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
The primary role of the gut is to digest food and absorb nutrients. Without a healthy gut, your body cannot effectively extract the vitamins, minerals, and energy it needs to function. Gut imbalances can lead to digestive issues like bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and malabsorption of nutrients.
2. Immune System Regulation
Approximately 70% of your immune system resides in your gut. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is responsible for mounting immune responses against harmful invaders while tolerating beneficial microbes and nutrients. A compromised gut can lead to increased susceptibility to infections and autoimmune conditions.
3. Mental Health and Brain Function
The gut-brain axis refers to the bidirectional communication between your gut and brain, primarily through the vagus nerve. The gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters like serotonin (often called the “feel-good” hormone), which influence mood, anxiety, and cognitive functions. Poor gut health has been linked to depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative disorders.
4. Metabolism and Weight Management
Your gut microbiome plays a role in regulating metabolism and fat storage. Certain bacterial species influence how your body processes food and stores energy. Imbalances in the microbiome have been associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
5. Skin Health
Conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis are often linked to gut health. An imbalanced gut can trigger systemic inflammation, which may manifest as skin issues. Healing the gut is a critical step in addressing chronic skin conditions.
6. Chronic Disease Prevention
An unhealthy gut can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation, a key contributor to diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and even cancer. Maintaining gut health is essential for reducing inflammation and promoting long-term wellness.
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
How do you know if your gut needs attention? Here are some common signs of poor gut health:

- Persistent bloating, gas, or indigestion
- Frequent constipation or diarrhea
- Food intolerances or sensitivities
- Chronic fatigue or low energy
- Frequent illnesses or infections
- Skin issues like acne or eczema
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Mental health struggles, such as anxiety or depression
- Autoimmune conditions or inflammatory disorders
Factors That Impact Gut Health
Several factors can disrupt the delicate balance of your gut microbiome, including:
1. Diet
- Processed foods: Diets high in sugar, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats can promote the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Low fiber intake: Fiber feeds beneficial bacteria, so a lack of it can reduce microbial diversity.
- Artificial sweeteners: Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners like aspartame may negatively impact gut bacteria.
2. Antibiotics and Medications
Antibiotics can wipe out both harmful and beneficial bacteria, leading to imbalances. Other medications, such as NSAIDs and proton pump inhibitors, can also affect gut health.
3. Stress
Chronic stress disrupts the gut-brain axis and alters the composition of the microbiome.
4. Sleep Deprivation
Poor sleep quality can negatively impact the gut microbiome and disrupt its circadian rhythm.
5. Environmental Toxins
Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins can harm gut bacteria.
How to Improve Gut Health
Now that we understand the importance of gut health, let’s dive into practical ways to support a healthy gut:
1. Adopt a Gut-Friendly Diet
- Eat more fiber: Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes are rich in fiber, which feeds beneficial bacteria.
- Include fermented foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso contain probiotics that help populate the gut with good bacteria.
- Limit sugar and processed foods: These can fuel harmful bacteria and cause imbalances.
- Consume prebiotic foods: Prebiotics, found in onions, garlic, bananas, and asparagus, act as food for probiotics.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration supports the mucosal lining of the gut and the growth of beneficial bacteria.
2. Take Probiotics and Prebiotics
Consider supplementing with probiotics to restore the balance of gut bacteria. Pair them with prebiotic supplements for maximum benefit.
3. Manage Stress
Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or spending time in nature. Reducing stress levels can improve gut-brain communication.
4. Get Enough Sleep
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a calming bedtime routine.
5. Exercise Regularly
Moderate exercise promotes gut health by increasing microbial diversity and reducing inflammation.
6. Avoid Overuse of Antibiotics
Use antibiotics only when necessary and take them as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Consider probiotics during and after a course of antibiotics.
7. Limit Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can harm gut bacteria and damage the intestinal lining.
The Future of Gut Health Research
The study of gut health is still in its infancy, and researchers continue to uncover new insights. Emerging areas of interest include:
1. Personalized Nutrition
Advances in gut microbiome testing may allow for tailored dietary recommendations based on an individual’s unique gut profile.
2. Microbiome Transplants
Fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) are already being used to treat conditions like Clostridium difficile infections. Future applications may include treatments for obesity, autism, and depression.
3. Psychobiotics
These are probiotics specifically designed to benefit mental health by targeting the gut-brain axis.
Final Thoughts
Your gut is the foundation of your health, influencing everything from digestion to immunity to mental well-being. By prioritizing gut health through a balanced diet, stress management, and lifestyle changes, you can improve not only your physical health but also your quality of life.
Remember, gut health is a journey, not a quick fix. Small, consistent changes can have profound impacts over time. If you’re dealing with persistent gut issues, consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist to develop a personalized plan for healing your gut.
Your body is an interconnected system, and the gut is at its core. Treat it well, and it will reward you with vitality and resilience. Let your gut health journey begin!