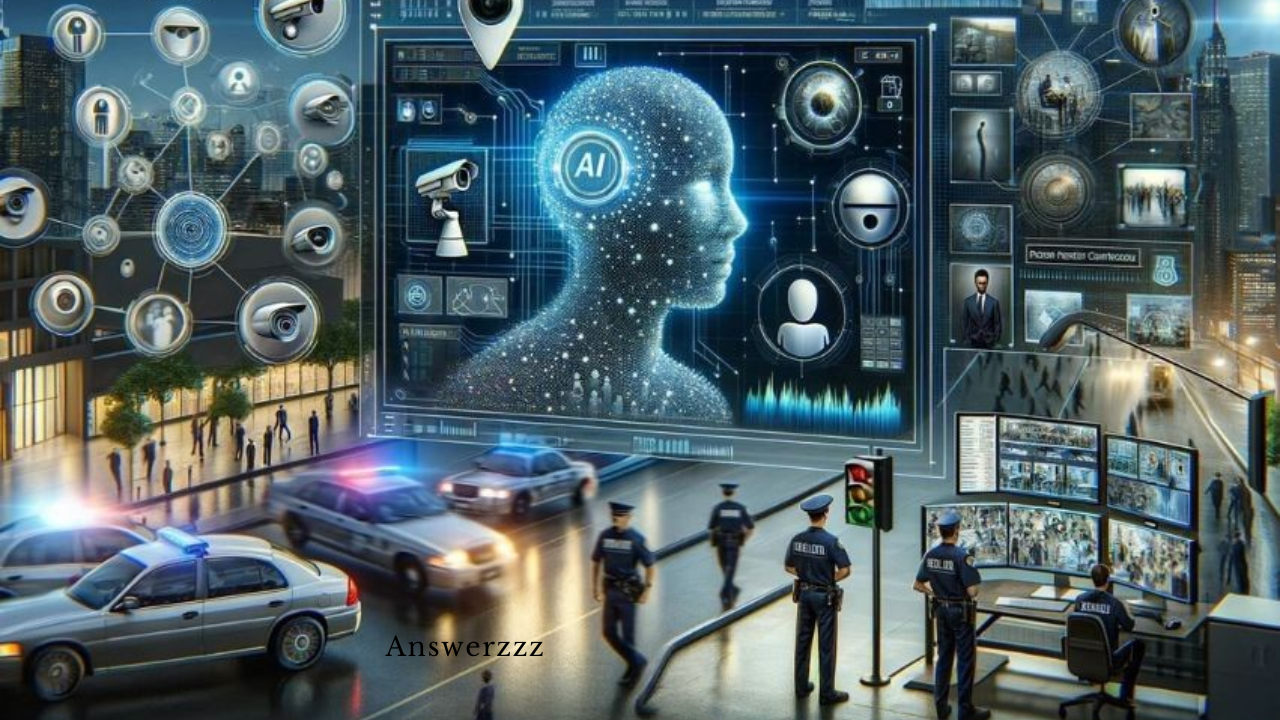
As technology advances, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in public safety has become increasingly important, especially in predicting and preventing crime. By analyzing massive datasets, AI algorithms are now capable of identifying trends, and patterns, and even potentially predicting criminal activities before they occur. This revolution in policing and public safety has the potential to reshape how law enforcement agencies operate, making communities safer and enabling proactive rather than reactive responses. This article explores the various applications of AI in crime prediction and prevention, along with ethical considerations, challenges, and the future of AI-driven crime prevention strategies.
1. The Evolution of AI in Law Enforcement
AI technology has grown from simple data analysis tools into sophisticated machine learning (ML) models capable of complex tasks. Originally used primarily in data storage and retrieval, AI now empowers law enforcement with advanced techniques in predictive analysis and real-time crime tracking. By analyzing data from diverse sources—such as criminal records, geographic information, and social media—AI enables law enforcement to see patterns they may otherwise miss. The shift from traditional policing methods to data-driven approaches marks a turning point in crime prevention and public safety.
2. How AI Predicts Crime
Predictive policing is one of the most discussed applications of AI in public safety. This approach uses data-driven algorithms to forecast where crimes are likely to occur, which helps law enforcement allocate resources more effectively. Here’s how AI is used to predict crime:
- Historical Data Analysis: Machine learning algorithms examine past crime data to identify trends and patterns that could predict future incidents. For example, if a particular area experiences a spike in burglaries during certain times, AI models can predict when similar crimes might occur again.
- Geospatial Analysis: AI tools analyze the locations of past crimes, taking into account socio-economic data, time of day, weather conditions, and more, to identify high-risk areas.
- Social Media Monitoring: By scanning public social media platforms, AI algorithms can identify keywords, patterns, or signals that might indicate planned criminal activities or gathering locations for potential violent events.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows AI to analyze text data from police reports, 911 calls, and other written sources. This technology can help identify patterns in language that correlate with specific types of crime.
Predictive policing models fall into two categories: location-based algorithms and person-based algorithms. Location-based models focus on identifying high-crime areas, while person-based models assess the likelihood of individuals committing a crime, using factors like past criminal records, social associations, and behavioral patterns.
3. Real-world applications of AI in Crime Prevention
Numerous cities and law enforcement agencies have adopted AI-driven tools to enhance public safety. Here are some real-world applications:
- ShotSpotter Technology: This system uses a network of acoustic sensors to detect and locate gunshots. When a gunshot is detected, law enforcement is notified in real-time, allowing for a rapid response. ShotSpotter is used in many U.S. cities and has contributed to quicker response times to violent crimes.
- Facial Recognition for Identification: AI-powered facial recognition systems are used to identify individuals at crime scenes or locate suspects in large crowds. While this technology has sparked privacy concerns, it remains a valuable tool for locating missing persons and apprehending suspects.
- Predictive Analytics Platforms: Some cities have implemented predictive policing software like PredPol, which analyzes historical crime data to forecast potential crime hotspots. By allocating more police resources to these areas, cities have reported reductions in certain types of crime.
- Social Media Monitoring for Threat Detection: AI tools like Babel Street analyze social media platforms for suspicious keywords and phrases that may indicate potential criminal activities, such as terrorism or planned violent protests. This monitoring allows law enforcement to act on potential threats before they occur.
4. Benefits of AI in Crime Prevention
The advantages of AI in crime prevention are significant, impacting both law enforcement and public safety outcomes:
- Resource Allocation: AI allows police departments to allocate resources more effectively by identifying high-risk areas and peak times for certain crimes. This efficiency leads to better utilization of limited personnel and equipment.
- Improved Response Times: Real-time data analysis and alerting systems enable faster response times. For example, in the case of gunshot detection systems, law enforcement can respond within minutes, potentially saving lives.
- Crime Pattern Recognition: AI’s ability to identify crime patterns helps law enforcement understand the underlying causes of crime in specific areas, facilitating targeted interventions and community engagement.
- Preventative Action: The predictive capabilities of AI allow for preventative policing. Rather than merely responding to crime, law enforcement can anticipate potential issues and intervene early, which can reduce crime rates.
- Enhanced Public Trust: Transparent AI-driven initiatives that show positive outcomes in crime reduction can increase public trust in law enforcement, particularly when these tools are seen as contributing to fairer and more effective policing.
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the potential of AI in crime prevention, there are substantial challenges and ethical issues that need to be addressed:
- Privacy Concerns: AI technologies like facial recognition and social media monitoring can infringe on personal privacy. Citizens may feel that constant surveillance violates their rights, and law enforcement must find a balance between public safety and privacy.
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inadvertently reinforce existing biases, especially if trained on biased datasets. For instance, if historical crime data reflects racial or socio-economic bias, predictive policing models might disproportionately target minority communities, leading to unfair treatment and over-policing.
- Transparency: Many AI models used in policing are proprietary, meaning the exact mechanisms of prediction are not always clear to the public or even law enforcement agencies. Lack of transparency can reduce public trust and make accountability difficult.
- False Positives and Misidentifications: Predictive models are not infallible, and false positives can have serious consequences, including wrongful arrests. Facial recognition technology, for instance, is less accurate for certain demographic groups, which raises concerns about potential errors and discrimination.
- Legal and Ethical Accountability: As AI plays a larger role in policing, questions arise about accountability. If an AI system makes an error or contributes to an injustice, it can be difficult to assign responsibility, which may lead to legal and ethical challenges.
6. Strategies for Ethical AI Implementation in Public Safety
To address the challenges associated with AI in crime prevention, law enforcement agencies can adopt the following strategies:
- Bias Mitigation: Ensuring that AI algorithms are trained on diverse datasets can reduce the risk of bias. Regular auditing of algorithms for fairness and accuracy can also help.
- Transparency and Accountability: Law enforcement agencies should make efforts to explain how AI tools are being used, the data they are based on, and the outcomes of AI-driven policing. In addition, accountability structures must be put in place to address any errors or misuse.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with communities and stakeholders about the use of AI in crime prevention can help build public trust. Law enforcement agencies should work with community leaders to address concerns and educate citizens on how these tools work and their intended benefits.
- Privacy Safeguards: Implementing robust data privacy policies is essential to protect citizens’ rights. Data collected by AI systems should be used solely for public safety purposes and stored securely to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Assessment: AI technologies and their impacts should be reviewed regularly to ensure they remain effective and ethical. Performance metrics, audits, and public feedback should be used to refine AI models and prevent potential misuse.
Revolutionizing UX Design with AI: The Future of User Experience
7. The Future of AI in Public Safety
The future of AI in public safety promises further integration of advanced technologies to improve the effectiveness and accuracy of crime prevention strategies. Some anticipated developments include:
- Real-Time Data Integration: The next generation of AI crime prevention tools may integrate real-time data from various sources, such as traffic cameras, body cameras, and drones, to provide a comprehensive view of public safety threats.
- Behavioural Analysis: AI may soon be able to detect behavioural cues that indicate criminal intent. By analyzing body language and facial expressions, AI could identify suspicious behaviour in crowded areas, allowing law enforcement to intervene before crimes occur.
- Enhanced Predictive Analytics: Advances in machine learning and data processing may lead to even more accurate crime predictions. Combining demographic, economic, and environmental data with crime records could provide deeper insights into crime drivers and risks.
- Interagency Data Sharing: Improved data-sharing protocols across federal, state, and local agencies could enable a more coordinated approach to crime prevention. AI could facilitate the synthesis of data from multiple sources, leading to a holistic understanding of crime trends and patterns.
- Smart Cities and IoT Integration: As cities adopt smart technology, AI-driven public safety systems will have access to a wealth of IoT data, from sensors to surveillance systems. This real-time connectivity could enhance the accuracy of crime prediction models and emergency response systems.

AI is revolutionizing public safety by transforming how law enforcement agencies predict and prevent crime. From predictive policing to real-time monitoring, AI tools offer significant benefits in reducing crime rates, optimizing resources, and enhancing public safety. However, with these advancements come ethical and practical challenges, including bias, privacy concerns, and the need for transparency. By prioritizing ethical AI implementation and fostering community engagement, society can leverage the full potential of AI in public safety while safeguarding civil rights. As AI technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an even more integral role in creating safer communities and a more proactive approach to crime prevention.