The digital revolution is reshaping industries at an unprecedented pace, and one of the cornerstones of this transformation is the concept of the Digital Twin. In the era of Industry 4.0, where cyber-physical systems and the Internet of Things (IoT) integrate seamlessly, digital twins are emerging as a powerful tool to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making capabilities. This comprehensive guide explores the role of digital twins in Industry 4.0, their benefits, use cases, and future potential.
What is a Digital Twin?
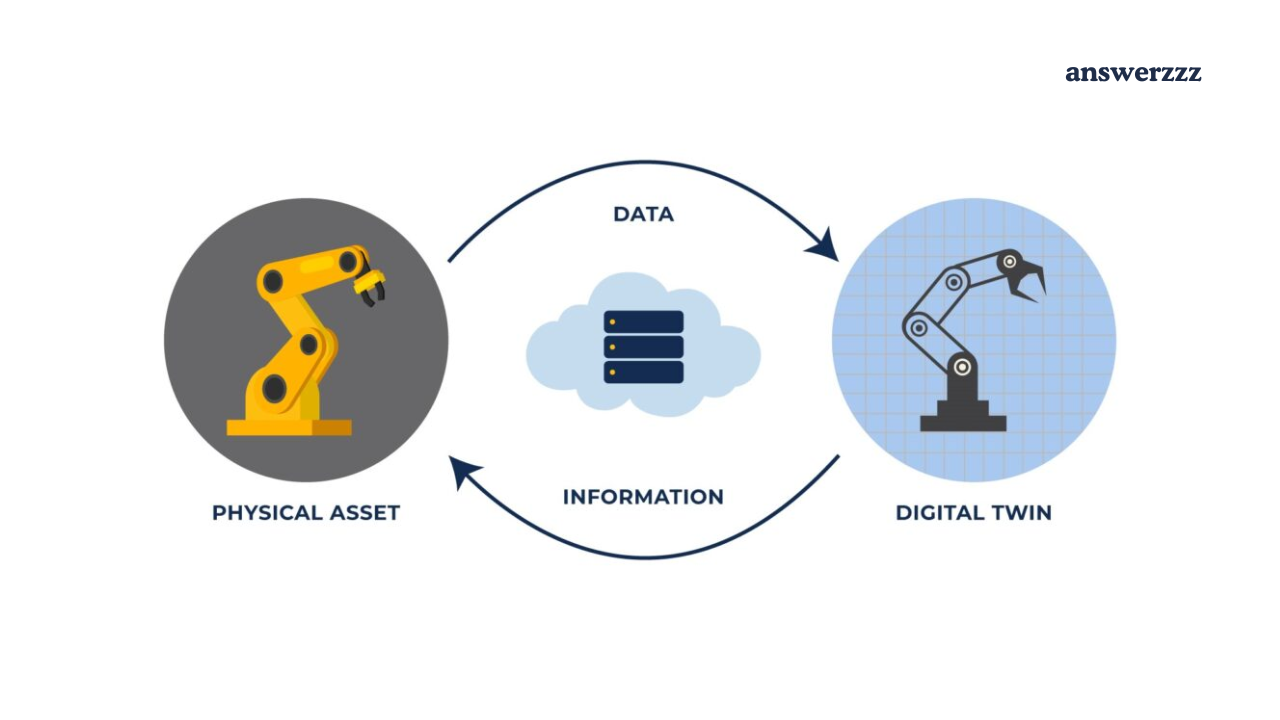
A Digital Twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, system, or process. It mirrors real-world entities in real time using data collected from sensors and connected devices. This allows companies to simulate, analyze, and predict the behaviour of physical assets under various conditions without physical trials.
Digital twins integrate several advanced technologies, including IoT, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Cloud Computing. By harnessing these technologies, digital twins provide a holistic view of the asset’s performance throughout its lifecycle, enabling continuous monitoring, optimization, and predictive maintenance.
Understanding Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is characterized by the fusion of digital, physical, and biological worlds through cyber-physical systems, IoT, and smart automation. It represents a new level of organization and control over the entire value chain, leading to smart factories and intelligent manufacturing processes.
The key components of Industry 4.0 include:
- IoT and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things): Connects devices and systems, allowing for real-time data collection and exchange.
- Big Data and Analytics: Enables analysis of vast amounts of data for better decision-making.
- AI and ML: Drives automation and predictive insights.
- Cloud Computing: Provides scalable resources for data processing and storage.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Assists in visualizing data and enhancing user interactions.
Digital twins lie at the heart of Industry 4.0, enabling manufacturers to create intelligent digital models of their assets and processes, offering unprecedented insights and control.
How Digital Twins Work
How Autonomous Vehicles Are Shaping the Transportation Industry in 2026
Digital twins are created by combining data from physical sensors with advanced simulation and analytics software. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Data Collection: Real-time data is gathered from sensors, IoT devices, and other connected assets.
- Data Integration: This data is integrated into a digital model, forming the virtual counterpart of the physical asset.
- Simulation: The digital model is used to simulate different scenarios, predict future performance, and test various configurations.
- Analysis and Optimization: AI and ML algorithms analyze the data to identify inefficiencies, predict failures, and optimize performance.
- Feedback Loop: The insights gained from the digital twin are fed back to the physical asset for real-time adjustments and improvements.
The continuous flow of data between the physical and digital twins enables a dynamic relationship that evolves, mirroring changes in the real-world entity.
The Role of Digital Twins in Enhancing Efficiency
1. Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is one of the most significant benefits of digital twins. By continuously monitoring asset performance and using AI algorithms, digital twins can predict when a component is likely to fail. This allows for timely maintenance, reducing unplanned downtime and extending the asset’s lifespan.
Example: In the aerospace industry, digital twins of aircraft engines are used to monitor wear and tear in real time. By predicting potential issues before they occur, airlines can schedule maintenance more effectively, reducing flight delays and cancellations.
2. Operational Efficiency and Process Optimization
Digital twins help optimize industrial processes by providing detailed insights into every stage of production. By simulating various scenarios, companies can identify bottlenecks, test process improvements, and make data-driven decisions.
Example: In manufacturing, digital twins of production lines can be used to simulate changes in workflow, enabling companies to optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
3. Improved Product Design and Development
By creating digital prototypes of products, manufacturers can test new designs virtually before physical production. This accelerates the design process, reduces the need for costly physical prototypes, and allows for faster time-to-market.
Example: In the automotive industry, digital twins of vehicle components are used to simulate crash tests, analyze aerodynamics, and optimize fuel efficiency. This helps car manufacturers produce safer and more efficient vehicles.
4. Enhanced Quality Control
Digital twins enable real-time monitoring of product quality during the manufacturing process. By comparing the digital model with the physical product, manufacturers can detect deviations early and make necessary adjustments, ensuring consistent quality.
Example: In the electronics industry, digital twins of circuit boards are used to monitor assembly processes and identify defects, reducing the rate of faulty products reaching the market.
Use Cases of Digital Twins in Industry 4.0
1. Smart Manufacturing
In smart factories, digital twins are used to create virtual representations of entire production systems. These digital models allow for real-time monitoring, simulation of different production scenarios, and optimization of the manufacturing process.
Example: Siemens uses digital twins to monitor its manufacturing processes. The digital twin of its electronics factory in Amberg, Germany, continuously analyzes data from the production line, enabling real-time adjustments to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
2. Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
Digital twins provide end-to-end visibility across the supply chain, helping companies track inventory, monitor shipments, and predict potential disruptions. This leads to better demand forecasting, improved inventory management, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Example: DHL uses digital twins to simulate its supply chain operations. By analyzing various scenarios, they can optimize route planning, reduce delivery times, and cut down on transportation costs.
3. Asset Management in the Energy Sector
In the energy sector, digital twins are used to monitor and manage complex assets like wind turbines, oil rigs, and power plants. By analyzing data from sensors, companies can optimize asset performance, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance safety.
Example: GE Renewable Energy uses digital twins of wind turbines to monitor their performance in real time. By predicting potential failures, they can schedule maintenance more effectively, reducing downtime and maximizing energy output.
4. Smart Cities and Infrastructure
Digital twins are also being deployed in smart city initiatives to model urban infrastructure. By creating digital replicas of buildings, bridges, and transportation systems, city planners can simulate various scenarios, optimize resource usage, and improve public services.
Example: Singapore has developed a digital twin of the entire city, known as Virtual Singapore. This digital model helps city officials analyze traffic patterns, plan new infrastructure projects, and manage emergency responses more effectively.
Challenges in Implementing Digital Twins
Top 5 Smart City Innovations Making Urban Living Easier in 2026
While the potential of digital twins is immense, there are several challenges that companies face when implementing this technology:
1. Data Integration and Management
Creating an accurate digital twin requires integrating vast amounts of data from multiple sources. Ensuring data quality, consistency, and real-time updates can be challenging, especially when dealing with legacy systems.
2. Cybersecurity Risks
Digital twins rely on constant data exchange between the physical and digital worlds, making them vulnerable to cyber threats. Companies need robust security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
3. High Implementation Costs
Developing and maintaining digital twins can be expensive, particularly for complex assets or processes. The high cost of sensors, data storage, and advanced analytics tools can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
4. Scalability Issues
As the number of connected devices and assets increases, scaling digital twins to accommodate large data volumes and complex simulations can be challenging. Companies need scalable solutions and infrastructure to handle the growing demand.
The Future of Digital Twins in Industry 4.0

The future of digital twins looks promising, with advancements in AI, ML, and cloud computing set to enhance their capabilities further. Here are some trends to watch:
1. AI-Driven Digital Twins
The integration of AI will enable digital twins to become more autonomous, providing predictive insights and real-time decision-making capabilities without human intervention.
2. Edge Computing Integration
With the rise of edge computing, digital twins can process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time responsiveness. This will be particularly beneficial in industries like manufacturing and healthcare, where real-time insights are critical.
3. Wider Adoption in Various Industries
While digital twins are already used in sectors like manufacturing, aerospace, and energy, their adoption is expected to expand to new industries, including healthcare, retail, and agriculture.
4. Enhanced Interoperability
Future digital twins will likely be more interoperable, enabling seamless integration across different platforms and ecosystems. This will create a unified digital landscape, enhancing collaboration and data sharing across industries.
Digital twins are a transformative technology that is driving the evolution of Industry 4.0. By creating virtual replicas of physical assets and processes, companies can enhance efficiency, improve product quality, and optimize operations. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits make digital twins a compelling investment for businesses looking to stay competitive in the digital age.
As technology continues to advance, digital twins will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of industries, paving the way for a smarter, more connected world. By embracing this innovative approach, companies can unlock new levels of productivity and efficiency, setting the stage for the next wave of industrial innovation.